Keywords: hydraulic breaker troubleshooting, excavator breaker attachment

hydraulic breaker troubleshooting
hydraulic breaker troubleshooting
When troubleshooting a hydraulic breaker attachment for an excavator, here are some common issues to consider and potential solutions:
Lack of Power: If the hydraulic breaker is not delivering sufficient power or impact force, check the excavator’s hydraulic system for proper flow and pressure. Low flow or pressure can result in reduced breaker performance. Ensure that the hydraulic lines and connections are not clogged or restricted.
Hydraulic Leaks: Inspect the hydraulic breaker and its connections for any signs of leaks. Leaks can result in reduced performance and potential damage to the attachment. Tighten loose connections or replace damaged seals to address the issue.
Excessive Heat: If the hydraulic breaker becomes excessively hot during operation, it may indicate an issue with the hydraulic system, such as inadequate oil flow or a clogged oil cooler. Check the hydraulic fluid levels and ensure proper cooling of the system to prevent overheating.
Excessive Vibration or Noise: Unusual vibrations or excessive noise during operation can indicate worn or damaged components in the hydraulic breaker. Inspect the breaker for any signs of wear or loose parts, and replace or repair as necessary.
Breaker Tripping or Stalling: If the hydraulic breaker frequently trips or stalls during operation, it may be due to excessive material hardness or improper use of the attachment. Ensure that you are using the appropriate breaker for the task at hand and adjust the operating settings accordingly.
If troubleshooting the hydraulic breaker proves challenging or the issues persist, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek assistance from a qualified technician or service professional who specializes in hydraulic attachments.
excavator breaker attachment
Excavator Breaker Attachment
An excavator breaker attachment, also known as a hydraulic breaker or hydraulic hammer, is a powerful tool designed to break and demolish hard materials such as concrete, rocks, and asphalt. It is typically mounted on the arm or boom of an excavator and powered by the excavator’s hydraulic system. The breaker attachment utilizes hydraulic pressure to deliver high-impact blows, shattering and fragmenting the material.
Excavator breaker attachments come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different excavator models and applications. They are commonly used in construction, demolition, quarrying, and mining projects to efficiently break up concrete structures, remove old pavement, and break rocks for excavation or site preparation.
When operating an excavator breaker attachment, it is crucial to follow proper safety guidelines and use the appropriate size and type of breaker for the task at hand. Regular maintenance and inspection of the attachment are also essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
CheckPoint
| Checkpoint (Cause) | Remedy |
| 1. Spool stroke is insufficient. After stop engine, depress the pedal and check if the spool moves full stroke. | Adjust pedal link and control cable joint. |
| 2. Hose vibration becomes bigger at hydraulic breaker operation. The high-pressure line oil hose vibrates excessively. (Accumulator gas pressure is lowered)The low-pressure line oil hose vibrates excessively. (Backhead gas pressure is lowered) | Recharge with nitrogen gas or check. Recharge with gas. If the accumulator or back head is recharged but gas leaks at once, the diaphragm or charging valve may be damaged. |
| 3. Piston operates but does not strike the tool. (Tool shank is damaged or seizing) | Pull out the tool and check. If the tool is seizing, repair with a grinder or change the tool and/or tool pins. |
| 4. Hydraulic oil is insufficient. | Refill hydraulic oil. |
| 5. Hydraulic oil is deteriorated or contaminated. Hydraulic oil color change to white or no viscous. (white-colored oil contains air bubbles or water.) | Change all hydraulic oil in the hydraulic system of the base machine. |
| 6. Line filter element is clogged. | Wash or replace the filter element. |
| 7. Impact rate increases excessively. (Breakage or maladjustment of valve adjuster or nitrogen gas leakage from the back head. ) | Adjust or replace the damaged part and check nitrogen gas pressure in the back head. |
| 8. Impact rate decreases excessively. (Backhead gas pressure is excess.) | Adjust nitrogen gas pressure in the backhead. |
| 9. Base machine meander or weak at traveling. (Base machine pump is the defective improper set of main relief pressure.) | Contact base machine service shop. |
Troubleshooting Guide
| Symptom | Cause | Required action |
| No blowout | Excessive nitrogen gas pressure of the back head Stop valve(s) closed Lack of hydraulic oil Wrong pressure adjustment from relief valve Faulty hydraulic hose connection Hydraulic oil in back head infection | Re-adjust nitrogen gas pressure in back head open stop valve Fill hydraulic oil Re-adjust setting pressure Tighten or replace Replace back head o-ring, or seal retainer seals |
| Low impact power | Line leakage or blockage Clogged tank return line filter Lack of hydraulic oil Hydraulic oil contamination, or heat deterioration Poor main pump performance nitrogen gas in back head lower Low flow rate by misadjustment of valve adjuster | Check linesWash filter, or replace Fill hydraulic oil Replace hydraulic oil Contact authorized service shop Refill nitrogen gas Re-adjust valve adjuster Push down tool by excavator operation |
| Irregular impact | Low nitrogen gas pressure in accumulator Bad piston or valve sliding surface Piston moves down/up to blank blow hammer chamber. | Refill nitrogen gas and check the accumulator. Replace diaphragm if need Contact authorized local distributor Push down tool by excavator operation |
| Bad tool movement | Tool diameter incorrect Tool and tool pins would be jammed by tool pins wear Jammed inner bush and tool Deformed tool and piston impact area | Replace tool with genuine parts Smoothen rough surface of tool Smoothen rough surface of inner bush. Replace inner bush if need Replace tool with new |
| Sudden reduction power and pressure line vibration | Gas leakage from the accumulator Diaphragm damage | Replace diaphragm if need |
| Oil leakage from front cover | Cylinder seal worn | Replace seals with new |
| Gas leakage from back head | O-ring and/or gas seal damage | Replace related seals with new |
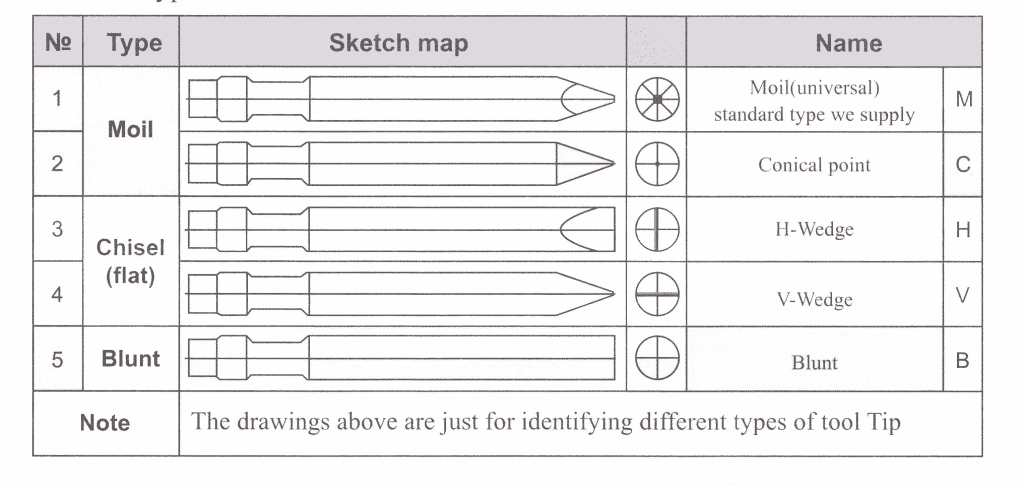
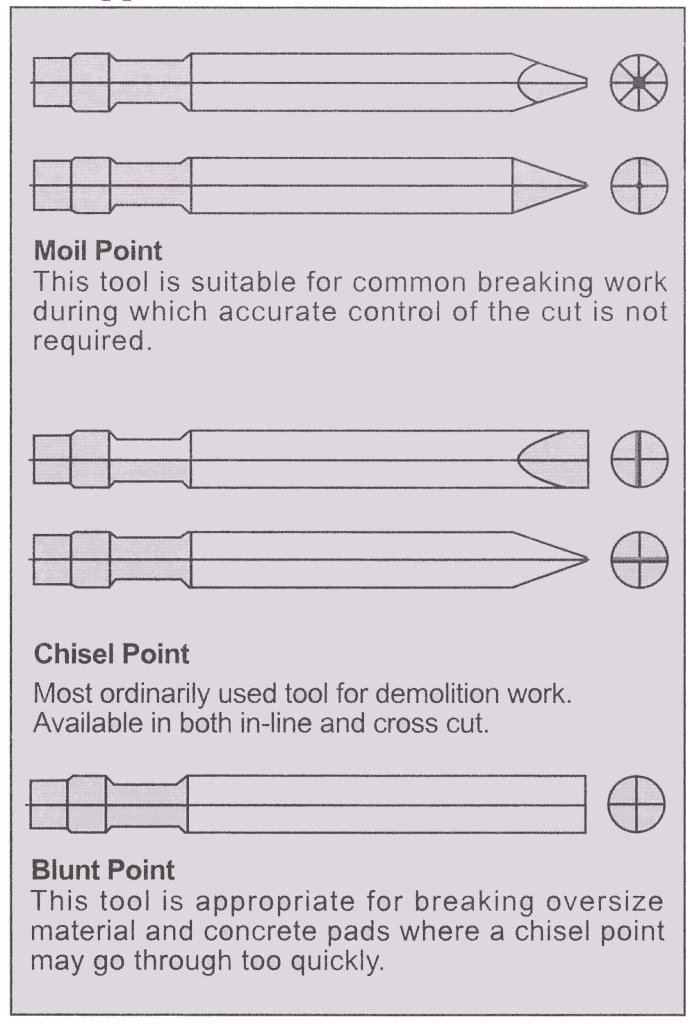
Guide to tool choice
Tool Type
Application Instruction
| NO | Model | Dia(mm) | Length(mm) | Weight(kg) |
| 1 | 45 | 45 | 500 | 8 |
| 2 | 53 | 53 | 580 | 10 |
| 3 | 68 | 68 | 702 | 18 |
| 4 | 75 | 75 | 710 | 22 |
| 5 | 85 | 85 | 745 | 29 |
| 6 | 100 | 100 | 1055 | 57 |
| 7 | 135 | 135 | 1200 | 119 |
| 8 | 140 | 140 | 1300 | 136 |
| 9 | 150 | 150 | 1300 | 160 |
| 10 | 155 | 155 | 1500 | 190 |
| 11 | 165 | 165 | 1500 | 224 |
| 12 | 165F | 165 | 1500 | 224 |
| 13 | 175 | 175 | 1600 | 260 |
Tool Dimension
Tool claim judgment
Hence, to help users use our products correctly, and ensure long operating life, these claim judgment criteria present defect examples that can occur during use, and the disposition standards applicable in each case.
Breakage of piston impact area or tool pins contact corners
Breakage of piston impacting point or of tool pins contact corners is extremely rare. This phenomenon occurs or when striking force is being concentrated on the tool corners due to unsatisfactory flatness of piston and tool impacting point. If such defect occurs, affected tools may not be accepted under warranty.
Plastic deformation of piston impact area
The possibility of tool tip plastic deformation occurring due to piston is extremely slim. Such defects may occur due to material strength deficiency, or brittleness, resulting from unsatisfactory heat-treatment. If such defect occurs, affected products may be accepted under warranty.
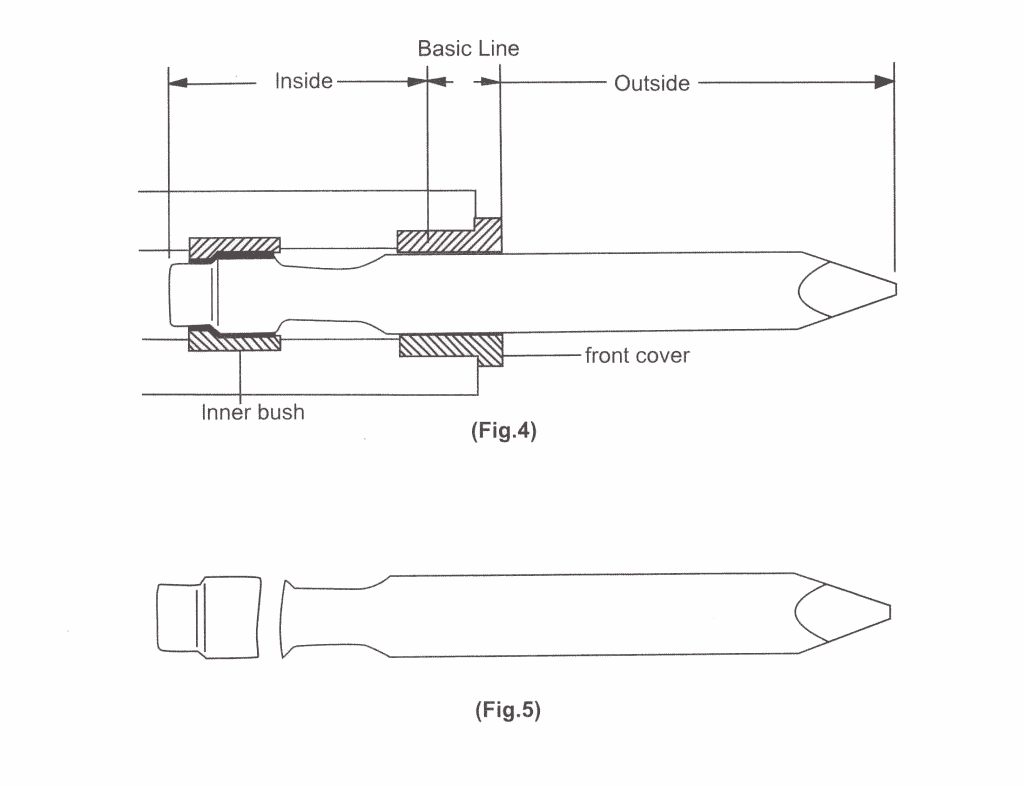
Breaking inside basic line
Should product breakage occur in any direction at a point inside the front cover, as shown in <Fig.5>, from the basic line shown in <Fig.4>, this may be due to defective material, defective heat-treatment; tool deformation, or unsatisfactory shaping of tool neck. Should such defect occur, affected products may be adopted under warranty.
In addition to the causes described above, product breakage inside the basic line may also occur if the interval between the front cover and tool widens due to excessive wear of front cover, coupled with excessive bending load being applied to hydraulic breaker, if any trace of seizure, caused by friction between the front cover and tool, is observed on the surface of the tool body, and if it is clear that product breakage is centered around the area of such seizure, affected products may be rejected under warranty.